Recommend Articles
The abuse of antibiotics has led to the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria, and new targets of antibiotics need to be developed urgently. FtsZ protein is a key protein in bacterial cell division, and inhibition of its dynamic process can lead to abnormal bacterial cell division and inhibition. In order to find bacterial inhibitors with new mechanisms of action, we conducted a virtual peptide screening by targeting the FtsZ protein ofStaphylococcus aureus, and calculated the root mean square deviation (RMSD) and interaction energy of the screened peptides for evaluation. We investigated their binding stability, tested the antibacterial activity of the hit peptides, and measured their effects on GTPase to explore their mechanism of action. The screened five peptides, TE101, PE101, PE102, PE103 and PE104, were tested in combination with the results of molecular docking and molecular dynamics analysis. The results showed that these five peptides inhibited the growth ofS. aureus, but did not act by affecting the GTPase of FtsZ protein.
The study of species abundance in forest community can not only reveal the maintenance mechanism of community biodiversity, but also provide theoretical basis for biodiversity conservation. In order to have an in-depth understanding of the distribution characteristics of species abundance patterns in forest communities along the latitude gradient, four representative forest communities within the latitude range of 21-42°N were selected. Species abundance distribution models based on pure statistics, neutral diversity theory and niche theory were adopted for fitting analysis, and further analysis was carried out in combination with the change characteristics of community diversity. The results showed that α diversity in each forest community decreased with the increase of latitude at this latitude gradient. In terms of species abundance model fitting, there was no difference in latitude gradient, and the fitting results showed that the metacommunity zero-sum multinomial distribution model in the neutral biodiversity theory had the best fitting effect. With the increase of latitude, the number of common and rare species in the community decreased gradually. The fitting results of rare species abundance distribution were consistent with the optimal community species abundance distribution model, while the fitting results of common species abundance distribution showed that the broken stick model in the niche theory had a better fitting effect. The proportion of rare species in tropical rainforest community is higher, which is more likely to cause species loss when disturbed, and thus has higher conservation value.
In order to solve the problem of where to plant mangroves in Hainan Island and how to plant mangroves to increase sinks, based on bioclimate, hydrology, geology and land use data, based on the maximum entropy (MaxEnt) model evaluation of the suitable growth area of mangroves in Hainan Island, the potential expansion area of mangroves in Hainan Island was predicted. Combined with the potential expansion range and the carbon density survey data of mangrove ecosystems in different regions, the InVEST model was used to estimate the increase of carbon storage of mangrove ecosystems in Hainan Island. The results show that: 1) The combination of MaxEnt model and InVEST model can well predict mangrove carbon storage, and the prediction of potential distribution areas of mangroves reaches high reliability (AUC > 0.96); 2) The current carbon storage of mangrove ecosystem in Hainan Island was about 1.24 Tg, of which soil carbon was about 0.84 Tg, the total carbon density was 217.01 t·hm−2, and the soil carbon density was 147.43 t·hm−2. Taking the largest mangrove distribution area of 12 506 hm2in Hainan Island as the control line of potential expansion range, it is theoretically that the mangrove ecosystem in Hainan Island can contribute about 1.25 Tg to the carbon neutrality goal under the upper limit scenario, while the increase in carbon storage of about 0.38 Tg can be achieved under the scenario of the lower limit of expansion, which only guarantees the completion of the basic task of expanding 2 000 hm2mangrove forest in the special action plan for mangrove protection and restoration (2020—2025)
The autophagy pathway activated by bacteria has two faces in maintaining the dynamic balance between intracellular bacterial removal and proliferation. On the one hand, cells recognize and remove intracellular bacteria via autophagy; on the other hand, bacteria evolve various escape mechanisms to inhibit and utilize autophagy to promote their own proliferation. A comprehensive summary was made of the complex relationship between bacterial infection and autophagy, involving the activation of autophagic pathways by bacteria, autophagic response pathways, the interaction between bacteria and autophagy, and the regulation of autophagy in the treatment of infectious diseases to review recent advances in bacterial infection and autophagy, as well as the utilization of autophagy, so as to provide reference for subsequent autophagy exploration.
A germplasm survey ofCamellia oleiferawas made in tropical areas of China from October to December 2021, and their geographical distribution, habitats, morphological characteristics, and correlation and variability with the economic traits were analyzed for evaluation. A total of 230 tropicalCamellia oleiferagermplasm resources were collected in 18 cities and counties in three provinces (Hainan, Guangxi, and Guangdong). The analysis showed that theC. oleiferagermplasm resources collected in the 18 cities and counties in the three provinces had an annual average temperature of 21.2 to 24.3℃, an annual average precipitation of 1,304.2 to 2,684.0 mm, and an altitude of 0.56 to 1,090.00 m. A total of 33 species of companion plants forC. oleiferawere found, among which 29 species were plants of angiosperms. The fruit were mainly multicolored, and mostly spheroid or citrus-like in shape, and the leaf shape index was significantly different. The variation coefficients of 11 economic traits ranged from 11.03% to 145.10%, among which the variation coefficient of the leaf shape index was relatively stable. Fruit peel thickness was the most important economic trait, and was significantly positively correlated with fruit diameter, fruit height, fresh fruit weight, fresh seed weight, fresh seed yield, number of seeds, and thousand kernel weight. There was a significant correlation between fruit peel thickness and leaf shape index.
The subcellular localization and expression analysis of Psbp proteinMePPD3(Manihot esculentaPsbP domain-containing protein 3, Phytozome database number: Manes.05G127800) were performed to explore whetherMePPD3is involved in disease resistance of cassava.MePPD3gene was amplified by RT-PCR. Sequence analysis showed thatMePPD3gene was 807bp in length, encoding 268 amino acids, with PsbP domain located at position 106-266 aa. Bioinformatics analysis ofMePPD3protein was conducted by NetPhos 3.1 Server, SignalP 5.0 Server, TMHMM Servervr, PSIPRED and PHYRE2 online, respectively. The results indicated thatMePPD3protein contained 32 phosphorylation sites, 5 glycosylation sites, and 1 transmembrane domain. The secondary structure of the protein was composed of 21.3% Helix (Helix), 26.5% fold (strand) and 52.2% random curl (loop). The multiple sequence alignment, phylogenetic tree analysis and conserved domain analysis indicated thatPPD3protein had a high genetic relationship among different plants. Subcellular localization showed thatMePPD3protein was localized in chloroplast. QRT-PCR results revealed that the expression level ofMePPD3gene in different cassava tissues was significantly different, and was the highest in mature leaves. In addition, the expression of this gene was induced byXanthomonas phaseolipv.manihotis(Xpm), indicatingMePPD3is involved in the resistance of cassava toXpm. AfterMePPD3gene was silenced by VIGS technique, the leaf lesion area of silent plants was significantly smaller than that of the control plants, which implies thatMePPD3negatively regulates cassava resistance to bacterial fusarium wilt caused byXpm.
In order to meet the increasing demand for high-quality fish protein and environmental protection requirements, a pilot intensive three-loop recirculating freshwater aquaculture system (RAS) was developed in Qionghai, Hainan province, China. Backwashing water from a microfilter is used as the carbon source for the denitrification process, and an operation mode is established to ensure the treatment of water quality and fish sludge to comply with the requirements for fish growth and pollution control. Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) was cultured in the pilot three-loop freshwater RAS for 121 days in an aquaculture experiment, and the fish growth, water quality and microbial communities in the system were observed and analyzed. The results showed that the tilapia had a survival rate of 100%, with the stocking density and the feed conversion ratio (FCR) being 107.7 kg·m−3and 1.74, respectively. The average concentrations of total ammonia (TAN), nitrite (NO2−-N) and nitrate (NO3−-N) were 0.95, 0.15 and 43.01mg·L−1respectively. The volume for daily water drainage was 2.66% of the total water volume in the system, and 6.67% of the water volume in the fish tank. No fish sludge was discharged throughout the experiment, and only a small amount of sludge existed in the anaerobic digestion unit by the end of the experiment. Microbial community analysis showed that a total of 21 genera of microorganism were involved in nitrogen metabolism, includingRhodobacte,FlavobacteriumandAzospira. These results implicated that the recirculating aquaculture system provides a potentially sustainable and ecological aquaculture mode for freshwater fish such as tilapia.
To clarify the spatiotemporal dynamics of the thripsMegalurothrips usitatusBagnall populations and the differences of the thrips populations in adult body size in Hainan, China and screen high effective insecticides for control of thrips eggs and pupae a systematical investigation was made into the annual occurrence ofM. usitatuson cowpea in Hainan, the adult body size of theM. usitatuspopulations at different geographical locations were measured, and the toxicity of various insecticides against the eggs and pupae ofM. usitatuswas tested by using the dip method and POTTER bioassay, respectively. The investigation showed thatM. usitatusoccured throughout the year in Hainan. Population dynamics were significantly regulated by host phenology and temperature. The adult body size measurement showed that the adult body length and body width ofM. usitatuspopulations were significantly higher in Danzhou than in Sanya and Chengmai. The toxicity test showed that the insecticide spirotetramat had a higher ovicidal activity (LC50=18.51 mg·L−1) againstM. usitatuseggs, while the insecticides spinosad and chlorfenapyr had a higher activity againstM. usitatuspupae, with theirLC50values being 26.18 and 27.71 mg·L−1, respectively. These insecticides could hence be recommended as candidates for controllingM. usitatuseggs and pupae in the field.
In order to provide a certain theoretical basis for the ecological risk assessment of pesticide tetrachlorantraniliprole, the concentration change of tetrachlorantraniliprole in water for 96 hours was determined by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. According to the OECD standard, zebrafish embryos were used as assessment of the model organisms. After static exposure to different doses of tetrachlorantraniliprole, zebrafish embryos were observed in terms of growth and development, and their voluntary movement, melanin and body length were calculated. The 96 hLC50were evaluated by mortality rate. Genes related with the melanin biosynthesis in the embryos were determined by using the RT-qPCR. The results showed that the tetrachlorantraniliprole in water for 96 h had the highest degradation rate (7.6%), with its concentration being greater than 80%, and had a good stability in water for 96 h. TheLC50of tetrachlorantraniliprole at 96 h was 23.775 mg•L−1, indicating low toxicity. The exposure to tetrachlorantraniliprole affected the development of zebrafish embryos in voluntary movement frequency, hatching rate and body length. The frequency of voluntary movement of zebrafish embryos increased with the tetrachlorantraniliprole concentration. When the exposure concentration was 39.8 mg•L−1, the zebrafish embryos had a voluntary movement frequency of 5.5 times•min−1, which was 22 times that of the control. When the exposure concentration was 27.65 mg•L−1, the zebrafish embryos decreased their hatching rate by 75%. At an exposure concentration of 39.8 mg·L−1, zebrafish decreased its body length by 32.27% compared with the control. Moreover, during the experiment it was also found that melanin pigmentation decreased after exposure to tetrachlorantraniliprole, and that the melanin area of 96 h zebrafish embryos decreased significantly with the increase of tetrachlortraniliprole concentration, and was reduced by 65% at the highest exposure concentration of 39.8 mg·L−1as compared with the blank control. The RT-qPCR results showed that the expression ofTyr,Sox10,Trp-1a, andMitfagenes had certain changes. The results showed that tetrachlorantraniliprole inhibited the expression ofSox10andMitfa, resulting in abnormal expression of tyrosinase-related transcription factors such asTyrandTyr-1a, which ultimately led to the impairment of melanin synthesis and pigmentation in zebrafish embryos.
Activated carbon (AC) was prepared from sludge and betel nut, and then loaded with FeCl3to prepare FeCl3-activated carbon (FAC). The physical and chemical properties of the prepared activated carbon before and after modification were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, specific surface area, FTIR infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results showed that the Fe3+was successfully absorbed onto the surface of the activated carbons. Compared with AC, FAC increased to some extent its porous structure and surface area, and its functional groups changed significantly. FAC had a good adsorption capacity for methylene blue when pH value of the water was between 4 and 10. The adsorption isotherms of the two activated carbons fitted the Langmuir model, and the maximum adsorption capacities of FAC and AC were 341.30 and 133.33 mg·g−1, respectively. Moreover, the adsorption kinetic of the two activated carbons conformed to the second-order kinetic model. Thermodynamic calculation showed that AC and FAC are endothermic and spontaneous in adsorption process of dyes (methylene blue) in the water. Thus, FAC can be used as a biosorbent to remove dyes from contaminated wastewater.
An attempt was made to explore the environmental quality and heavy metal contamination of agricultural land soil in Hainan Island. The surface soil samples from 133 agricultural lands in the whole island were collected to evaluate the soil heavy metal contamination and ecological risk in the study areas by using the geological accumulation index method and the potential ecological risk index method. The results showed that 83.46% of the soil sampling sites in the agricultural land of Hainan Island were unpolluted with low geological accumulation index of 8 heavy metals Cd, Cr, Zn, Pb, Cu, Ni, Hg and As, while 7.52% of the sampling sites were slightly polluted mainly by Cd, Cr and Cu, and 4.51% of the sampling sites were moderately polluted largely by Ni. The agricultural land soil in Hainan Island has a low contamination degree of heavy metals, and the potential ecological risk of heavy metals was very low in all the sampling sites. The main potential hazardous element was Cd, and the sampling sites with moderate and heavy risk of Cd were 21.80% and 3.76%, accounting for the largest proportion of the heavy metals. This indicates the soil of agricultural land is enriched with Cd in some sampling sites. It is concluded that the soil environmental quality of agricultural land in Hainan Island is generally good, although some agricultural land in Hainan has moderate ecological risk of heavy metals in soil, mainly in the south of Ding'an County, the north of Chengmai County, and the junction of Changjiang County and Dongfang City.
With the widespread application of image acquisition equipment and data sharing platform, the amount of bird image data has been increasing at an unprecedented speed. How to effectively deal with such a large amount of data has become a major challenge. In recent years, convolutional neural network has shown strong practicability and effectiveness in the application of automatic bird image processing. However, there has been no research on automatic recognition of movements in wild birds. In view of this, a special action image dataset of the sandpiper was established based on field images. The dataset was composed of nine action tags representing the main behavior patterns of spoon-billed sandpipers (Eurynorhynchus pygmeus). At the same time, three residual convolutional neural network models, ResNet50, ResNetT101 and ResNet152, were used to automatically recognize the movements of the spoon-billed sandpipers. The experimental results show that the three models achieved excellent results in action recognition with their accuracy rates of the test set being 96.90% (ResNet50), 96.94%(ResNet101) and 96.90% (ResNet152), respectively. This indicates that these three models have a rapid recognition of the movements of the spoon-billed sandpiper.
Indoxacarb belongs to oxadiazine insecticide, which blocks the insect sodium channel. Lepidopteran pests, such asCotton Bollworm,Plutella xylostella, andSpodoptera litura, were effectively controlled by indoxacarb. The scholars have focused on the selective toxicity of indoxacarb isomers to non-target organisms. In this study the acute toxicity of indoxacarb and its isomers, (+)-S-indoxacarb and (-)-R-indoxacarb, on the silkwormBombyx moriwas evaluated by spray method. Additionally, the toxic effects of indoxacarb and its isomers on the silkworm were evaluated by measuring the changes in the activities of antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD) in the silkworm. The results showed that the 96 h-LC50of indoxacarb, (+)-S-indoxacarb and (-)-R-indoxacarb to the silkworm were 0.379, 0.041 and 0.113 mg·kg−1mulberry leaf, respectively. The (+)-S- indoxacarb and (-)-R- indoxacarb were highly toxic to the silkworm. The 96 h-LC50of the (+)-S-indoxacarb was 2.750 folds higher than that of the (-)-R-indoxacarb, which suggested an enantioselective toxicity to the silkworms. The mixture of the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (-)-R-indoxacarb showed an antagonism effect with the co-toxicity coefficient being 12.868. The activities of SOD and CAT in the silkworm were significantly increased in the indoxacarb treatment groups, which induced oxidative stress in the silkworm. The activities of SOD significantly increased in the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (-)-R-indoxacarb treatment groups with the concentrations of 0.730, 1.460, and 2.920 mg·kg−1mulberry leaf. The activities of CAT significantly increased in the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (-)-R-indoxacarb treatment groups with all the concentrations except the concentration of 0.183 mg·kg−1. The activities of POD were decreased in all the indoxacarb treatment groups. The effect of indoxacarb on SOD, CAT and POD was lower than the sum of the individual effects of the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (-)-R-indoxacarb, indicating that the mixture of the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (-)-R-indoxacarb produced antagonistic effects on inducing of oxidative stress in the silkworm. The toxic effects of indoxacarb, (+)-S-indoxacarb and (-)-R-indoxacarb on silkworms were preliminarily evaluated, which provides reference for the application of indoxacarb in the field. This result suggests that the indoxacarb when sprayed in the field should be kept away from mulberry gardens to avoid harm to silkworms.
In order to explore the effects of different nitrogen sources on the growth and development of different cassava varieties and their differences, three different nitrogen sources, namely -N, NO3−and NH4+, were used to treat four cassava varieties,‘CH16’, ‘SC16’, ‘SC205’ and ‘17Q’, in the experiment. The growth status, nitrogen content, root morphology, nitrogen accumulation and nitrogen use efficiency of four cassava varieties were observed and analyzed. The results showed that under the treatment of NaNO3(3 mmol·L−1) and NH4Cl (3 mmol·L−1), the cassava varieties ‘SC205’and ‘17Q’ had a relatively higher nitrogen utilization efficiency for ammonium nitrogen, belonging to the ammonium preferred varieties, while ‘SC16’ and ‘CH16’ had no difference in nitrogen utilization efficiency and preference for nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen. Under the condition of no nitrogen, ‘17Q’ and ‘SC16’ were nitrogen efficient cultivars with relatively high resistance to low nitrogen stress, while ‘SC205’ and ‘CH16 ’were nitrogen inefficient cultivars with relatively low resistance to low nitrogen stress, among which ‘CH16’ had the lowest tolerance to low nitrogen. The study lays the foundation for genetic improvement of nitrogen use efficiency and scientific fertilization in cassava agricultural production.
To investigate the changes of metabolites in epidermal bladder cells of the halophytic speciesMesembryanthemum crystallinumunder salt stress, the metabolites in the epidermal bladder cells ofM. crystallinumunder control and salt stress were identified and analyzed by using the liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), and a total of 356 known metabolites were identified in the epidermal bladder cells. Analysis of differential metabolites showed that the levels of 37 metabolites in the epidermal bladder cells were significantly changed under the salt stress. Metabolic pathway enrichment analysis of the differential metabolites based on the KEGG database showed significant perturbations in six biochemical pathways defined in KEGG, such as phytohormone signaling, zeatin biosynthesis, purine metabolism, etc. These results indicate that salt treatment can cause significant changes in metabolites in epidermal bladder cells ofM. crystallinum.
Nauplii ofArtemia sp.are a common and important live larval feed used in fish seed production. To make clear the effect ofArtemiasp.nauplii as supplementary feed on the rearing of the juveniles of freshwater black angelfish (Pterophyllum scalare), the angelfish juveniles are selected and reared for 26 days in an experiment with two treatments to observe their growth performance. The juveniles were fed with commercial pellet feed withoutArtemiasp.nauplii as a control group (M), and with commercial pellet feed supplemented withArtemiasp.naupliias the other treatment group (MA).The results showed that the other treatment group improved the survival rate of the angelfish juveniles significantly due to supplementary feeding withArtemiasp.nauplii, and increased the specific growth rate, as compared with the control group. The survival rates were (95.53±3.21)% and (82.50±4.32)% for the other treatment group and the control group, respectively, and their specific growth rates were (8.50±1.47)%·d and (6.92±1.06)%·d, respectively. Supplementary feeding with the nauplii ofArtemia sp.is conducive to the growth of the qualitative and morphological traits of the angelfish juveniles, and increased the body length, condition factor, and uniformity of body length and weight of the angelfish juveniles in fish population. At the end of the experiment the juveniles were 25 mm in body length, 12 mm in height, 22 in pelvic fin length, 10 mm in dorsal fin height and 5 mm in caudal fin length, and their body length and the condition factor increased by 12 mm and 3%, respectively. The uniformity of body length and the uniformity of body weight in fish population were 92% and 90%, respectively. The finding is helpful to optimize the management and improve rearing techniques for freshwater black angelfish juveniles.
An attempt was made to analyze the impact of a split root treatment using two forms of nitrogen on efficiency of two varieties of cassava ('SC16' and 'SC205') in using nitrogen. Cassava roots were treated unilaterally with nitrogen (-N/+N) or bilaterally with nitrogen (+N/+N), and the differences in agronomic traits (biomass, plant height, root length, etc.) and nitrogen physiological indicators (nitrogen content, nitrogen accumulation, and nitrogen physiological use efficiency) between the cassava varieties SC16 and SC205 under different nitrogen sources (NO3−, NH4+) after one month of split root treatment were compared to find out the effect of split root treatment with two N forms on nitrogen use efficiency of the two cassava varieties. The results showed that the reduced total N application to cassava by half (-N /+N) did not affect the shoot/root ratio and whole plant weight, but promoted cassava plant height and at the same time increased obviously the root nitrogen accumulation, the ratio of nitrogen to root and the nitrogen use efficiency. The root development of the cassava on the N-added side was inhibited in the -N/NH4+treatment. Conversely, the –N/NO3−root-split treatment resulted in better root morphology on the NO3−-side, and it also increased shoot N accumulation and root N use efficiency. Under the unilateral root-split treatment with the same nitrogen source, the plant height, the biomass of shoot and root, the nitrogen accumulation of root and shoot, and root morphology of SC205 were better than those of SC16. The nitrogen use efficiency of the -N/NO3−treated SC205 was higher than that of SC16 in the shoot and root, while the nitrogen use efficiency of the -N/NH4+-treated SC205 was lower than that of SC16. All these results showed that unilateral root-split treatment with two forms of nitrogen at a half-reduced rate could improve the N use efficiency of the two varieties of cassava. The unilateral split root treatment with nitrate nitrogen was more conducive to the growth of SC16 and SC205 at the seedling stage, and SC205 under this treatment had higher nitrogen efficiency and better growth compared to SC16.
To explore a simple analytical method for identifying catechols and the types of their protecting groups, the colors of phenol and catechol with FeCl3in aqueous solutions and their visible absorption spectra were compared, and over thirty phenolic substances were tested for color developments with FeCl3on TLC silica-gel plates. Color-developing effectiveness between phenols and four metal chlorides were evaluated to establish a correlation between catechol concentrations and shades of spot colors. The kinetics of acetonide decomposition in dilute FeCl3ethanol solution were analyzed. The experiments demonstrated that phenols with weak binding abilities did not develop colors with FeCl3on TLC silica-gel plates while phenols with strong chelating abilities such as catechol did. The greenish/bluish black color on the spots of catechol samples arose from the mono- and bi-coordinated Fe(III) complexes, not from the tri-coordinated ones. Since FeCl3is a strong Lewis acid and can selectively cleave phenol protections, catechols protected by various types of protecting groups showed different color changes. Catechols protected by weak-acid labile protecting groups exhibited slow color development at room temperature; those protected by strong-acid labile protecting groups displayed no color at room temperature but bluish-black after heated on the silica-gel plate at 110℃ for 5 min; those protected by strong-acid stable protecting groups showed no color change under both conditions. The results also indicated that FeCl3was the best color-developing agent among the four metal chlorides in testing phenols, with the optimum concentration of the phenols ranging from 10 to 50 mmol·L−1.
To investigate the impact of sea surface temperature gradients on severe convection, Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model is used to simulate a severe convection event occurred in the northeast of the South China Sea on 14 August 2010.The characteristics of water vapor transport, wind field and ground surface heat flux were analyzed during the development of severe convection by comparing a control run (CNTL) with a sensitivity experiment (EXP). Results show that ocean warm eddy and high SST gradient can stimulate convergence or divergence and enhance moisture transport by changing local thermal conditions, which cause release of latent heat providing energies for the evolution of severe convection. The precipitation regions correspond to the high SST center and the strong SST gradient area. The high (low) SST gradients can cause changes in sensible heat flux and latent heat flux, thus strengthening (inhibiting) precipitation.
In order to investigate the effects of hypoxic-induced-factor-1α (HIF-1α) on the immune response of the hemolymph ofLitopenaeus vannameiunder hypoxia stress, dsRNA was injected intoL. vannameito interfere with the expression ofHIF-1αgene under the hypoxic stress (2.0 mg·L−1) to analyze the regulation effect of hypoxic stress onHIF-1αgene expression level in the hemocyte ofL. vannamei. Immune indicators such as hemocyte counts, hemocyanin concentration, gene expression level, enzymatic activity, etc were determined. The results showed that the expression level ofHIF-1αin the RNA interference group decreased by 80.1% compared with the control group. The hemocyte counts were significantly lower under hypoxic conditions in the interference group compared with the control group (P< 0.05). Additionally, the concentration of hemocyanin was significantly higher in the interference group than in the control group (P< 0.05). The expression levels ofAstakine(AST) andhemocyte homeostasis-associated protein(HHAP) in the hemocytes were significantly higher in the RNA interference group under hypoxic conditions than in the control group, while the expression levels ofFerritin(FT) in the hemocytes were not significantly different between both the interference and control groups. The enzymatic activities of ACP, AKP and PO in the serum in the RNA interference group under hypoxic conditions were reduced to different degrees. By interfering with the expression ofHIF-1αgene, it was found thatHIF-1αgene played an important role in hemocyte counts, hemocyanin concentration, expression of immune-related genes and the activity of immune-related enzymes inL. vannamen.
The structure and function of seagrass ecosystems were changed and the diversity and service function of the seagrass ecosystems were affected by the top-down regulation of herbivorous effects on the seagrass. Different herbivores have different effects on resource allocation of the above ground and below ground parts of the seagrasses due to their different feeding capacity.Thalassia hemprichii, a dominant seagrass in Hainan Province, was selected to simulate the response of functional traits (root-shoot ratio, biomass and element content) to herbivoring effects onT. hemprichiiby setting up isolation cagein situand placing chemical expellant (Sevin) to exclude feeding effects of different consumers on the seagrass. The results showed that the root-shoot ratio of the seagrassT. hemprichiiincreased with time, but there was no significant difference in root-shoot ratio between different treatments. Grazing by consumers reduced the biomass ofT. hemprichii. The above ground biomass ofT. hemprichiiin the treatment (MF) with exclusion of two consumers, both gastropods and fish, was higher than that of the blank control treatment (CK) without excluding consumers. Herbivory increased the above ground seagrass allocation ratio of organic carbon and total nitrogen to maintain normal growth ofT. hemprichii, but the herbivorous impact on the total phosphorus content was not significant (P> 0.05). In general, herbivorous effects increased the root-shoot ratio and regulated the allocation of biomass, organic carbon, total nitrogen, and total phosphorus in above ground and below ground parts ofT. hemprichii, which was used to improve the absorption and assimilation rate of the resources, avoid grazing by the consumers, and maintain the population ofT. hemprichii.
In order to improve the concentration and quality of genomic DNA extracted from the striped mealybug (Ferrisia virgata), the adults of the striped mealybug were collected on the same day and soaked in 95% alcohol for 7 days, and their genomic DNAs were extracted from a gradient of 1, 3, 5, 7 and 10 adults by using different combinations of two kits and three pre-treatment grinding methods. The concentration and OD value of the extracted genomic DNAs (A260/A280) were estimated and evaluated. The results showed that when 10 adults were used for extraction under the combination of TIANGEN kit and grinding pestle + grinding instrument as pretreatment, the concentration and quality of the genomic DNAs of the striped mealybug were high; the OD value (A260/A280) was 1.80-1.90; the gel band was clear. Compared with other combinations (1.95-2.20), this combination extracted genomic DNA with the least impurities and contamination.
In order to understand the prevalence ofHepatozoon canisdisease in Hainan in recent years, the prevention and control measures were evaluated for better control of Canine hepatozoonosis in Hainan. There were 1039 dog blood samples collected from 18 cities and counties in Hainan Province from October 2017 to May 2022, and they were detected forH. canisby PCR. Among the dog blood samples collected, 135 samples were found to be positive forH. canis, with an infection rate of 13.0%. Of the samples higher infection rates ofH. caniswere found in Haikou (20.7%), Sanya (20.6%), Tunchang (33.3%), and some infections ofH. caniswere also found in Wenchang (8.7%), Dingan (5.6%), Chengmai (6.3%), Danzhou (5.0%), Qiongzhong (15.8%), Ledong (18.8%) and Changjiang (6.7%). The positive samples from Sanya (OP699205), Ledong (OP699206), Dingan (OP699207) and Qiongzhong (OP699208) were selected to construct a phylogenetic tree based on the 18S rRNA of theH. canis. It was found that the homology ofH. canisin Hainan was the closest to that ofH. canis(AF176835) in India, which was 99.85%, and was also separated from that of the branches ofH. felisandH. americanum. This shows that the dogs in Hainan Island has a high infection rate ofH.canis. The prevention and treatment ofH.canisrequires regular elimination of the transmission vectorRhipicephalus turanicus.
In order to obtain exogenously expressed antimicrobial peptide, cathelicidin-1 expression recombinant vector was constructed using molecular cloning technique, and the secreted cathelicidin-1 was expressed inPichia pastoris. The antimicrobial activity of the fermentation broth containing Cathelicidin-1 was evaluated. The full-length gene encoding cathelicidin-1 was synthesized by total DNA synthesis and amplified by PCR. The full-length gene was linked to the eukaryotic expression vector pGAPZαA, and the recombinant plasmid pGAPZαA-Cathelicidin-1 was transformed intoEscherichia coliDH5α for multiplication. The multiple plasmids were extracted, single digested, and transformed into the yeastPichia pastorisGS115. The transformed yeast was cultured in the YPD culture medium, and the fermentation broth was collected after 72 hrs of culture and used to express the antimicrobial peptide Cathelicidin-1 in a secreted form by using Tricine-SDS-PAGE. The antimicrobial activities of the fermentation broth were evaluated by using inhibition zone of the antimicrobial peptide and the microbial growth curve. Measurements of inhibition zone and growth curve showed that the fermentation broth from the yeast expressing Cathelicidin-1 exhibited significant inhibitory activity againstE. coli, but did not show any bacteriostatic effect onStaphylococcus aureus.
Water use efficiency (WUE), a critical element of carbon and hydrological cycle, plays a key role in land-atmosphere feedback. The seasonal differences of rubber plantation ecosystems in WUE from 2010 to 2019 were analyzed by using the EC-LUE model and the Penman-Monteith model based on the data of gross primarily productivity (GPP) and evapotranspiration (ET). Furthermore, the impact of each factor on the change of WUE was quantitatively evaluated. The factors were then classified into two groups: atmospheric (temperature, atmospheric pressure, water vapor deficit, net radiation, and solar radiation) and biophysical (fraction of photosynthetically active radiation, soil heat flux, aerodynamic resistance, and canopy resistance). The results showed that the rubber plantation ecosystems had a lower WUE (3.52 g·kg−1) in the rainy season than in the dry season (4.73 g·kg−1) from 2010 to 2019, and that both GPP and ET curves were clearly unimodal, with their peaks all in the rainy season. Solar radiation tended to reduce the increase of WUE in the dry season, indicating a negative contribution, although this suppression was counteracted by other atmospheric factors, showing a positive contribution. Surface impedance, which tended to encourage the growth of WUE in the dry season, had the highest contribution to WUE change, accounting for 33.29% of the total. The WUE change in rubber plantations from rainy to drought seasons were primarily governed by biophysical parameters, which might serve as a reference for a further study of the ecohydrological and carbon-water cycle activities in rubber plantations.
Drosophila suzukiiMatsumura is a worldwide fruit pest. Based on the transcriptome ofD.suzukii, five metabolic detoxification genes were identified by using sequence analysis, phylogenetic analysis, structural domain analysis and conserved motif analyses. These five genes include ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABCs), cytochrome P450 (CYPs), glutathione S-transferases (GSTs), carboxylesterases (CarEs) and UDP-glucuronosyl-transferases (UGTs). Phylogenetic analysis showed that CYPs genes were classified into four clans,CYP3,CYP4,CYP6andCYP9, while ABCs genes fell into four clans,ABCC,ABCD,ABCFandABCG. GSTs genes were classified intoGST-Delta,GST-Epsilon,GST-ThetaandGST-Zeta. The CarEs genes and UGTs genes ofD.suzukiiwere the closest to those ofDrosophila subpulchrella. Structural domain and conserved motif analyses showed that CYPs had a conserved P450 domain; ABCs had a conserved ABC2 domain; GSTs had a conserved GST domain; CarEs had a conserved Coestrases domain; UGTs had a conserved UDPGT domain. Conservative motifs of CYPs were EEGGKKRNDFLDLLJZLKKEG. Conservative motifs of ABCs were DCPSASNPADYIIE. Conservative motifs of GSTs were LYPKDLVKRAVVDQRLHFE.
The principles, methods and steps of multi-omics, including metabonomics, transcriptomics and proteomics technologies, were described, and the current status, future research directions and the advantages of high sensitivity and high throughput of metabonomics, transcriptomics and proteomics technologies in the interaction between mycoviruses and host fungi were comprehensively analyzed in combination with their research cases in hypovirulent mycoviruses. This review is helpful for deep exploration of the effects of mycoviruses on host fungi and their molecular mechanisms, and provides methods and ideas to determine whether mycoviruses can be used as biological factors for control of plant fungal diseases.
Germplasm is the basic material for breeding and selection. It is of great significance to understand various characters of germplasm and fully exploit the utilization value of the germplasm. Jaboticaba (Plinia cauliflora) germplasm is characterized by a high diversity of plant phenotypes including long fruiting, ornamental and unique flavors. Twenty-three jaboticaba cultivars introduced for planting in Hainan were used as materials for the evaluation of 16 traits including stamen shape, tree height, stem diameter, etc. The average coefficient of variation for the phenotypic traits tested was 23.35%. The highest mean coefficient of variation was 32.52% for jaboticaba cultivar Kembuka, while the lowest mean coefficient of variation was 17.81% for cultivar Esca. The diversity index for descriptive traits of 23 jaboticaba cultivars was 0.287 - 0.855. All these results showed that the introduced jaboticaba planted in Hainan had a high genetic diversity in phenotypic traits.
It is of great practical significance to carry out relevant research on mangrove plant population to understand the population structure and dynamics of mangroves at the present stage for improving mangrove conservation and ecological restoration. A survey ofRhizophora stylosapopulation in permanent sample plots covering 1 hm2in Dongzhaigan National Mangrove Reserve, Haikou, Hainan Province was made to analyze the population structure and dynamics ofR. stylosa. The analysis showed that the stem diameter structure of theR. stylosapopulation in these plots was of irregular pyramid type, with the total number of individuals in age class I to III accounting for 48.84% of the total number of individuals in the population, and the number of individuals in age class Ⅳ being significantly low. The population dynamic change index suggested that theR. stylosapopulation in this mangrove reserve is expanding, but not stable, and not significantly under external disturbance. The population had a Deevey type II survivorship curve. The static life table, mortality curve, disappearance rate curve and survivorship analysis of theR. stylosapopulation showed that the population dynamics in this mangrove reserve was relatively drastic at the younger stage, and relatively stable when the population developed into the older stage. The time series analysis of theR. stylosapopulation reveals that although there are more individuals at the lower age level in the current population, relatively few individuals will develop into the older age level after several age levels in the future, and that the future population will consist of individuals mainly at the middle and older age levels. The population ofR. stylosain Dongzhaigang National Mangrove Reserve is expanding, but is sensitive to external disturbance. The dynamic changes of the population are more intense in the lower age stage, and relatively stable in the middle and old stages. Therefore, the long-term monitoring and disaster prevention of the population should be strengthened, especially the protection and assisted restoration of the individuals at the younger stage.
To explore the role of sucrose non-fermentation associated protein kinase 2 (SnRK2) in the response ofHevea brasiliensisto low temperature stress, a member of the SnRK2 subfamily, namedHbSnRK2.7, was cloned from the leaves of the cold-resistant clone Reyan ‘93-114’ ofHevea brasiliensisby using RT-PCR. The gene cloned contains an open reading frame of 1 095 bp that encodes a protein of 364 amino acids.HbSnRK2.7has a conserved serine/threonine protein kinase domain with a molecular weight of 41.39 kD and an isoelectric point of 4.70. It is predicted that it can catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to the serine/threonine residues on the protein substrate, which is also the concentrated region of phosphorylation sites. It also has domains needed for abiotic stress and ABA-dependent domains for HbSnRK2.7 activation. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) results showed thatHbSnRK2.7gene was down-regulated in response to ABA induction. When treated with ABA for 8 h, the expression was down-regulated to the lowest point. Under low temperature stress, the expression ofHbSnRK2.7decreased significantly. The expression ofHbSnRK2.7was down-regulated continuously under low temperature stress for 4 h and 8 h, and the expression ofHbSnRK2.7was down-regulated to the lowest level at 24 h under low temperature stress, which was about 1/2 of non-stress expression. Moreover, the expression ofHbSnRK2.7was significantly higher in the cold-susceptible clones than in the cold-resistant clones. These results suggest thatHbSnRK2.7may act as a negative regulatory factor to mediate the formation of low temperature stress resistance ofHevea brasiliensisdependent on ABA.
In the Northern Hemisphere, leaf phenology is often reported to have a high spatial variability due to environmental differences at different latitudes. The duration of plant leaf phenology has an important impact not only on the carbon sequestration capacity of plants, but also on their reproductive success and ability to adapt to climate change. However, previous studies on population differences in leaf phenology often were only focused on the differences in leaf unfolding or leaf discoloration stages among different populations, and less attention was paid to the duration of leaf phenology and its driving mechanism. In this study, linear regression models were established by using the phenological data of the leaves of paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera). recorded by China Phenology Observation Network to analyze the latitudinal differences in the duration of phenology of the leaves. The analysis showed that with the increase of latitude, the leaf-unfolding stage for paper mulberry gradually advances and the leaf-falling period gradually delays, indicating that the leaf phenology duration for paper mulberry tended to be shortened with the increase in latitude. The analysis of the importance of environmental factors by using random forest regression showed that the temperature before the leaf-unfolding stage was the most critical environmental factor controlling the leaf-unfolding stage and leaf duration of paper mulberry, and that the precipitation prior to leaf fall was the most critical environmental factor at the leaf fall season, indicating that the latitudinal patterns in leaf phenology duration are jointly shaped by temperature and precipitation. All these results show that the phenology of widely distributed plants has obvious latitudinal gradients in different populations, so as to adapt to different local environmental conditions and improve their own adaptability. Studying the phenological differentiation of different populations of the same species from the perspective of latitudinal differences is helpful to assess the changes in the distribution range and extinction risk of species in the future.
It is of important basic data significance to understand the molecular structure and characteristics of opsin ofMegalurothrips usitatuspest by cloning Rhodopsin gene ofM. usitatusfor further analysis of light environment differences. The full-length gene of the rhodopsin,MuRhodopsin, was cloned based on the transcriptome information of thrips. The sequence homology was compared using DNAMan 9.0 and SWISSMODEL software, and the phylogenetic tree was constructed. The full-lengthMuRhodopsingene was 1140 bp, encoding 380 amino acids, with a relative molecular weight of 42.73 Da and a theoretical isoelectric point of 8.47. Sequence alignment and homology analysis showed thatMuRhodopsinwas rhabdomeric opsins (r-opsins) with high homology with that ofFrankliniella occidentalisandThrips palmi. The domain analysis showed that the protein had 7 transmembrane domains, including 1 G protein-coupled receptor family region, belonging to the G protein-coupled receptor family, and contained 6 N- cardamoylation sites, 3 N- glycosylation sites, 3 casein kinase II phosphorylation sites, and 4 protein kinase C phosphorylation sites. The 322nd amino acid lysine (K) of the protein is an important binding site to chromophore (retinal), which is a typical opsin that can activate the IP3/Ca2+ signaling pathway and cause light-dependent depolarization reaction. The structure and function ofRhodopsininM. usitatuswere elucidated, providing a theoretical basis for further study of its visual pathway.
The structural features of keratins, the three degradation methods for keratins including physical, chemical and biological degradation, and the utilization of degradation products were reviewed, and the three degradation methods were compared. Compared with the physical and chemical degradation methods, the biological degradation approach, especially the enzymatic hydrolysis method, has the advantages of environmental friendliness, low-cost, and high-value degradation products which can be effectively utilized in the sectors of medicine, industry and aquaculture. The recent research and application of keratinase from the perspectives of classification, developmental evolution relationship and degradation methods and modes were overviewed. At present, the existing research on keratinases needs to improve. For example, most of the selected keratinases are unable to degrade keratin alone without disruption of the keratin disulfide bond in a reducing environment. Or multiple different keratinases are used simultaneously to complete the degradation process. These shortcomings and deficiencies prevent the large-scale industrial application of keratinase. It is still the focus of future research to screen and purify more efficient keratinases tolerant of high temperature, acid and alkali to explore the molecular mechanism of keratin degradation by keratinases, and to make full use of keratinases for targeted cleavage of keratin to obtain high-purity and high-value-added degradation products.
Soil cadmium pollution has attracted more attention in China, and calls for safe and effective remediation. Previously, we obtained a high cadmium-resistant strainEnterobacter cloacaeLPY6 by domesticatingE. cloacaeCu6. The strain LPY6 was used to treat seeds and plants of wheat (Triticum aestivumL.) in seed germination and pot experiments to analyze its potential and mechanism in alleviating the toxicity of cadmium to wheat growth. The seed germination and pot experiments found that LPY6 could reduce the toxic effects of cadmium on wheat seed germination and seedling growth, and decrease the cadmium levels in plants. In addition, LPY6 can also reduce the free cadmium contents in liquid media and in soils, suggesting LPY6 can adsorb or uptake cadmium from the soils and reduce the adsorption of available cadmium by plants. This indicates that LPY6 may be a potential strain for bioremediation of cadmium pollution.
A survey ofPinus lattericommunity in Bawangling Ridge, Hainan was made by using sample plotting, and the species composition, geographic composition, community structure, and species diversity ofthe P. lattericommunity were analyzed to have clear understanding of the community structure and species diversity ofP. latteritherein. The survey indicated that theP. lattericommunity in Bawangling is rich in plant species and composed of 66 families, 146 genera, and 230 species, with Lauraceae, Euphoribiaceae, Rubiaceae as dominant families andP. latteriMason,Psychotria asiatica, andAporosa dioicaas dominant species. Dominating genus is not immediately apparent. The species diversity of theP. lattericommunity is different and varies along the altitudinal gradient, where the species richness index decreased with the rise of the altitude, and the Shannon-Wiener index, and Pielou index decreased and then increased with the rise of the altitude. TheP. lattericommunity has extensive phytogeographic associations, with its tropical distribution being dominant and containing one endemic genusCunninghamia. TheP. lattericommunity has a complex structure with a typical inverted "J" shape in diameter and height distribution, and the diameter and tree height ofP. latteriin the community are bell-shaped in structure, indicating that theP. lattericommunity is high in stability with good regeneration and can hence have a steady succession.
In order to provide a scientific basis for the rational planning of the spatial layout of Haikou, the ecosystem service value (ESV) and its changes in the urban fringe of Haikou, Hainan was estimated in 2005, 2009, 2015 and 2020 based on the equivalent factor method. With the aid of the grey linear programming model, the land use construction was optimized with the goal of maximizing ESV, and the changes of land use and ESV before and after the optimization were discussed. The results show that the area of construction land has increased year by year since 2005 while the arable land and wetland decreased. The total ESV increased first and then decreased, with a slight increase of 0.21%. The ESV of woodland was the highest among the lands, and the ESV of hydrological regulation was the highest among the single ecological service functions. After optimization, the total ESV value increased by 1.73%, the wetland and construction land increased, and the unused land decreased. The wetland ESV increased the most. The permanent basic farmland is protected when the demand of urban sustainable development is met.
To explore the resources and diversity of halophytes in the coastal area of Hainan Island, a general survey of the distribution of halophytes was conducted by using plot sampling, and the species and diversity of the halophytes were analyzed. The results showed that a total of 125 species halophytes belonging to 92 genera and 50 families were recorded, including 123 species in 91 genera and 49 families of angiosperms, and 2 species in 1 genus and 1 family of pteridophytes. There were fewer families with multiple species, more families with single species, and most families with 2~9 species accounting for 52% of the total number of families. The number of genera with single species was the largest, accounting for 78.26% of the total species. In terms of life form, the halophytes in Hainan Island included 23 species in 17 genera and 14 families of trees, 32 species in 29 genera and 20 families of shrubs and small trees, 63 species in 46 genera and 22 families of herbs, and 7 species in 7 genera and 4 families of vines. The halophytes are divided into 6 and 11 areal types of species and genera, respectively, with their tropical distribution being dominant. The salt-secreting plants were richest in the halophytes with 63 species according to the salt regulation system of halophyte types. Wenchang city was relatively rich in species, with a high diversity index but uneven distribution. There were many species of herbs in cities and counties. The halophytes have various uses in Hainan Island. It is concluded that the halophytes in the coastal area of Hainan Island are rich in species and high in diversity.
Our laboratory preliminarily identified WY172 and WY195 promoter sequences from the rubber tree powdery mildew fungus (Erysiphe quercicola), which could effectively driveGUSexpression in both monocotyledonous rice and dicotyledonous tobacco. In order to investigate whether WY172 and WY195 have promoter activity inE. quercicola, the pJNARG vector was used as a backbone, linking WY172-GFPand WY195-GFPto construct recombinant expression vectors (WY172-GFP and WY195-GFP vectors). The recombinant vectors were introduced intoColletotrichum siamenseinfecting rubber trees by protoplast transformation method. Fluorescence microscopy showed that both WY172 and WY195 could stably drive the expression ofGFPgene. And in different stages ofC. siamense, WY172 and WY195 could play promoter roles to stably drive the expression ofGFP. In addition, we changed the environmental conditions for the growth of anthracis and measured the GFP expression under different conditions. The results showed that the long light condition enhanced the activity of WY172 to driveGFPexpression, and that the activity of WY195 was improved by the long light treatment and the low temperature treatment at 23°C. This indicates that WY172 and WY195 have stable promoter activities inC. siamense, and that their activities can be induced by changing light or temperature conditions.
Infrared camera technology is increasingly used in wildlife diversity surveys and long-term monitoring, mainly focusing on the research of ground-dwelling birds and mammals, but less on highly arboreal endangered species, such as Hainan gibbons and associated species diversity. From January 2019 to June 2020, 66 infrared cameras were deployed in the forest canopy of the Hainan gibbon sympatric distribution area to explore the diversity of mammals and bird, the seasonality of activity intensity and changes with altitude gradients. A total of 10 species of mammals that belong to 3 orders and 4 families were recorded, of which 2 species were under national Class II protection. The three mammals with the highest relative abundance were Hainan gibbon (Nomascus hainanus) (RAI=58.44),Petaurista hainana(RAI=17.78) andDremomys rufigenis(RAI=14.34). There were 20 species of birds belonging to 6 orders and 11 families recorded, of which 10 species were listed under national Class II protection and three of them,Ducula badia,Treron curvirostraandGlaucidium cuculoides,were higher in relative abundance index (44.92, 20.23 and 6.74, respectively). Hainan gibbons andPetaurista hainanashowed similar monthly relative abundance, with their activities being high in the dry season and low in the wet season; while other mammals and birds were not significantly correlated with seasons. The diversity of mammals showed a monotonical decrease with the increase of altitude, and had the highest level of species diversity in the range of 600 ~ 800 m asl. The diversity index of birds first increased and then decreased with the increase of altitude. This study revealed for the first time the composition of companion birds and mammals in the same area where Hainan gibbons are distributed, providing a reference for habitat restoration and ecological corridor construction of Hainan gibbons based on animal diversity in the Bawangling area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park.
Huguangyan Maar Lake is endowed with a special geographical environment and has a great potential for exploring thermotolerant fungal resources in special habitats. A thermotolerant fungus HS1-1 was collected from Huguangyan Maar Lake, observed morphologically and identified molecularly, and its physiological properties, enzyme production capacity and antibacterial activity were determined. The results showed that the strain of this fungus is identified asAspergillus fumigatus. This fungus can grow at the temperatures of 15~50 ℃ and pH 3~12, and has an optimum growth at the temperature of 40 ℃, a salt concentration of 1%~2%, and pH 6~7. The fungus has a strong ability to utilize soluble starch, lactose and carboxymethyl cellulose, and has a certain inhibitory effect on five indicator bacteria, as determined by screening on four enzyme-producing media. This indicates that the fungus HS1-1 is high in thermotolerance and acid and base tolerance with some antibacterial activities. This study provides a theoretical basis for an in-depth understanding of the thermotolerant fungi of Huguangyan Marr Lake and their further development and utilization.
Oil palm (Elaeis guineensisJacq.) is an important tropical palm with high oil production. Fatty acyl-ACP thioesterase (FAT) is the key enzyme for hydrolysis of acyl and ACP and termination of carbon chain extension. The oil palmFATAfamily mainly acts on eighteen-carbon chain fatty acids (18: X-ACP), but the specific hydrolysis substrates and preferences are unknown. In this study, the full-length sequence of theEgFATAgene was first cloned from oil palm fruit. Bioinformatics analysis indicated that theEgFATAcoding region consists of 1155 bases and can encode 385 amino acids with a molecular weight of 91.89 kDa, and is most closely related to the algaPdFATA. A viral silencing vector forEgFATAwas constructed and then infected the embryoids of oil palm, and RT-qPCR results showed that the expression ofEgFATAwas down regulated by 85%-90%. At the same time, fatty acid GC analysis of the silenced embryoids showed that the contents of stearic acid (C18:0), oleic acid (C18:1) and linoleic acid (C18:2) were significantly reduced. The aforesaid results indicated thatEgFATAhad catalytic effect on the hydrolysis of C18:0-ACP, C18:1-ACP and C18:2-ACP in the oil palm embryoids, with the highest catalytic activity observed in the hydrolysis of C18:1-ACP. This study initially explored the biological functions ofEgFATAgenes in oil palm, providing a theoretical basis for further exploration of the molecular mechanisms ofEgFATAin regulation of lipid metabolism.
Leaf meal of giant duckweed (Lemna polyrhiza) variety DW2602 was used as a feed supplement in the conventional tilapia feed at a rate of 0%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and 30%, respectively, and fed to tilapia fingerlings at the feeding rate of 2.5%, 3%, and 4% of tilapia body weight for 40 days. The growth indexes of the tilapia fingerlings fed with the giant duckweed leaf meal as feed supplement, such as weight gain, specific growth rate, condition factor, viscerosomatic index, etc. were determined. The results indicated that the tilapia fingerlings fed with the tilapia feed supplemented with the giant duckweed leaf meal increased their crude protein content by 4.3%, reduced their crude oil by 0.9%, and enhanced their sulfur-containing amino acids (methionine and cysteine) by 0.1% as compared to those fed only with the conventional feed, and that no obvious change was measured in their lysine content. The giant duckweed leaf meal used as feed supplement promoted the growth of tilapia (P < 0.05). The conventional feed supplemented with 20% of giant duckweed leaf meal at a feeding rate of 3% of the tilapia body weight significantly promoted the growth of tilapia, and increased tilapia weight gain by 57.5% and the specific growth rate by 30.3% and reduced the condition factor and viscerosomatic index by 6.4% and 5.5%, respectively, as compared to the 100% conventional feed. This indicates that supplement of giant duckweed leaf meal in the conventional tilapia feed at a given rate promotes the growth of tilapia.
An attempt was made to study the therapeutic effect of alendronate sodium and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on canine Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (LCPD) to provide a new way for the clinical treatment of avascular necrosis of canine femoral head. Twelve 6-month-old dogs with similar body weight were selected to establish the LCPD model by liquid nitrogen freezing, and the modeling results were evaluated and staged by X-ray film and Ficat-Arlet classification system. According to the clinical diagnostic criteria, nine dogs with the stages I-II of avascular necrosis of the femoral head were randomly divided into three groups, A, B and C. Group A was treated with alendronate sodium orally; Group B received intra-articular injection of calcium gluconate activated platelet rich plasma; Group C served as a control group without any treatment. Three months after treatment, X-ray films were taken and the femoral head of the affected limb was dissected to evaluate the therapeutic effect. If the X-ray film shows no phase III and IV pathological features and anatomical results, and the surface of the femoral head is smooth without collapse, it is considered that the treatment is effective, otherwise it is ineffective. The results showed that the two dogs in Group A had effective treatment while one did not have effective treatment. All the three dogs in Group B were treated effectively, and the three dogs in Group C were not effectively treated. This indicated that both alendronate sodium and PRP can effectively treat canine LCPD, but there was no significant difference in treatment effect between alendronate sodium and PRP (P=0.267).
It has been demonstrated that exosomes derived from macrophages can be used as adjuvants to enhance cellular immune response. An attempt was made to explore whether exosomes derived from lipopolysaccharide-activated chicken macrophages could be used as immune adjuvants for the potential prevention and control of epidemic diseases in Wenchang chicken. The exosomes were extracted by ultracentrifugation and identified by transmission electron microscopy and particle size analysis. Subsequently, the exosomes were labeled with PKH67 dye and co-incubated with bone marrow-derived dendritic cells from Wenchang chicken. The uptake and activation of the exosomes by the dendritic cells were observed under a fluorescence microscope. The results showed that the exosomes derived from chicken macrophage HD 11 cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharides were ingested by amphioxus-derived dendritic cells and promoted the activation of dendritic cells.
The rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) infected with powdery mildew fungusErysiphe quercicolawill have a significant loss in natural rubber yield. Previous studies suggest that LFG proteins confer susceptibility to plants, and that the mutations on LFGs can inhibit invasions of powdery mildew fungi in barley (Hordeum vulgare) andArabidopsis thaliana. InH. brasiliensis, gene expressions of two putative LFG proteins including HbLFG1 and HbLFG2 respond to the pathogenic development of the powdery mildew. HbLFG1 negatively regulates plant immunity. However, the function of HbLFG2 was not known. In this context the function of HbLFG2 in plant immunity was investigated by using Agrobacterium mediated transformation inA. thalianaandNicotiana tabacum. The results showed that constitutive expressions of HbLFG2 inA. thalianaandN. benthamianainhibited reactive oxygen burst and callose deposition induced by bacteria flg22 (flagellin domain of a synthetic 22-amino-acid peptide). This function of HbLFG2 was similar to that of HbLFG1. Moreover, HbLFG2 could not inhibit the hypersensitive response induced by phytophthora elicitor INF1 or DTT (Dithiothreitol) but by Bax. It was different from HbLFG1. These results suggest that both HbLFG1 and HbLFG2 can inhibit plant immunity responses, but have different mechanisms for their functions.
Bacterial blight of rice is a bacterial disease caused byXanthomonas oryzaepv. oryzae(Xoo), and it occurs in a large area, causing serious damage, and is difficult to control. In our laboratory aBacillus velezensisstrain HN-2 with a strong biocontrol activity isolated from the paddy soil was found that its n-butanol extract has a strong inhibitory activity againstXoo. In order to study the inhibition mechanism of the n-butanol extract of the strain HN-2 onXoo,Xoowas treated with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 and bacitracin, respectively and analyzed by using transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq)., and the transcriptome data was then analyzed by using GO database and KEGG database. Transcriptome data analysis results showed that a large number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) inXooafter treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 and bacitracin. A total of 1512 DEGs were obtained after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2, 871 DEGs were up-regulated and 641 down-regulated. GO enrichment analysis found that after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2, the DEGs inXooare mainly clustered in the cell process, metabolic process, macromolecular complex, catalytic activities, etc. KEGG cluster analysis found that after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 the ribosomal pathway inXoocontained the largest number of DEGs while the other major metabolic pathways involved are starch and sucrose metabolism, benzoate degradation, glycerophospholipid metabolism, bacterial chemotaxis, etc. This suggests the n-butanol extract of HN-2 should have a main impact on the ribosomal pathway, and pathways of starch and sucrose metabolism and bacterial chemotaxis.
To reveal the pathogenesis ofEnterococcus faecalisand provide scientific basis for clinical treatment, several strains ofE. faecaliswere isolated from female vagina and their virulence genes, resistance genes, and drug resistance were detected by using PCR and Kirby Bauer (K-B) disk diffusion. The results showed that 22 strains ofE. faecaliswere isolated from 157 samples. Of the 22 strains isolated,efaA was the most commonly found virulence gene (100%), followed byasa1 (90.9%),cylA (90.9%),fsr(90.9%),cpd(90.9%),acm(86.4%),gelE (81.8%),esp(68.2%),ace(54.5%), andhyl(0), and the drug resistance genes detected werevanA (0),vanB (0),vanC (18.2%),aac(6')/aph(2')(40.9%),ant(6)-1(59.1% ),ermB (68.2%),mefA (54.5%),tetM (72.2%), andtem(81.8%). Antibiotic susceptibility testing by the K-B disk diffusion method showed that the isolates were sensitive to vancomycin, nitrofurantoin, linezolid and koalaranin, but resistant to other antibiotics in different degrees. To sum up, vaginas are susceptible toE. faecalisinfection, and experimentin vitroindicated that glycopeptide antibiotics were promising in the clinical treatment choice forE. faecalisinfection.
In order to reduce the risk of heavy metal pollution and ensure the safety of vegetable production, the heavy metal contents in the soil and the edible parts of 18 varieties under 5 types of vegetables were determined, and the status of heavy metal pollution in the vegetables were evaluated. Meanwhile an enrichment coefficient was used to analyze and compare the capacity of the vegetables to accumulate the heavy metals Cd, Cr, Pb, Zn, Cu, Ni, Hg and As. The results showed that the soil Cd content in the area under experiment was 31.91%, which was the main pollutant, while the contents of other heavy metals fell within the national standards. The edible parts of all vegetables were mainly contaminated, and garlic and rape, spinach and coriander were slightly contaminated by heavy metals Cr, Hg, and Cd. The enrichment coefficients of the 8 heavy metals in the vegetables showed that the average enrichment coefficient of the heavy metals in 18 varieties of vegetables was in the descending order of Cd > Zn > Hg > Cu > Ni > As > Cr > Pb. The average enrichment coefficient of Cd was 0.201 1 and Pb was 0.003 1, a difference of 64.66 times between Cd and PB. The enrichment coefficient of the same element in different vegetables showed significant difference which was up to 120 folds. Generally, leaf vegetables such as coriander had a relatively higher enrichment capacity for Cd, Hg, Pb, Cr, Ni, Zn, Cu, and spinach for As and Pb, which indicates that coriander and spinach in the experimental area should not be cultivated on the soil contaminated with Cd, Hg, Pb, Cr, Ni, Zn and Cu. Red rape should not be cultivated on the As and Pb contaminated soil, However, cabbage and root vegetables, such as cabbage, white radish and carrot, had a weak capacity to accumulate Cd, Hg, Cr, Pb, As, Ni and Cu; Cd, Cr, C n, Cu, Ni and Hg; and Zn, Cr, and Cu, respectively, and can hence be used as the priority varieties of vegetables cultivated in the soils contaminated with Cd, Hg, Cr, Pb, As, Ni, Cu, and Zn in the experimental area.
An attempt was made to reveal the cadmium enrichment characteristics ofPueraria thomsoniiplanted for different years. The plants ofP. thomsoniigrown for one year and two years on moderately cadmium-contaminated farmland in Xinyu, Jiangxi province were collected to determine the content and enrichment of the heavy metal cadmium in the tuber (meal and residues), basal stem, main stem, lateral branches, and leaves. Except for the leaves, the cadmium content was significantly higher in each part of the two years old plants than in the one year old plants. The contents of cadmium in different plant parts were in the order of lateral branch > main stem > basal stem > leaves > residues > tuber > meal.P. thomsoniihas a high capacity to absorb cadmium from soil, as evidenced by the enrichment coefficient of cadmium from soil toP. thomsoniibeing larger than 1. Except for the meal of the tuber from the one year old plants ofP. thomsonii, the cadmium contents in the tuber of 1-years old plants, and the tuber and meal of 2-years old plants were all higher than the limit of the standard. Correlation analysis showed that the content of cadmium in each part ofP. thomsoniihad a significantly positive correlation with the total and available cadmium in the soil and had an accumulative effect on the age of the plants. Therefore, in a moderately cadmium-contaminated farmland it is recommended to plantP. thomsoniifor one year and use its tuber to produce meal as food to attain both ecological and economic benefits.
Ticks are arthropods that transmit more types of pathogens globally than any other vector, and they can transmit a variety of diseases by sucking blood from mammals, birds and reptiles, including humans.Anaplasmaspp are an important tick-borne pathogens, which have a significant impact on human and animal health and the development of animal husbandry. In order to investigate the species of ticks on canine body surface and the situation of ticks carryingAnaplasmaspp. in some areas of Hainan province, morphological observation, molecular biological identification and evolutionary analysis were performed on canine ticks from four regions of Hainan province, and 16SrRNAandgltAgenes were used to detectAnaplasmaspp in canine ticks. Morphological observation and molecular biological identification showed that all the ticks wereRhipicephalus sanguineus. The phylogenetic tree established based on tick mitochondrial 16SrDNAgene indicated that the HN-01 and HN-02 gene sequences obtained were in different genetic evolutionary clade, and that HN-01 was in the same clade as the known tick from the United States (MH018842). HN-02 was in the same branch asR. sanguineusfrom Thailand (KC170744), and was far related toR. sanguineusfrom Gansu Province (JF979377) and Beijing (KC203362). PCR results based on thegltAgene showed thatA. platyswas carried by canine ticks with a positive rate of 1.1% (6/546). PCR detection based on 16SrRNAgene indicated that the canine body surface ticks obtained did not carryAnaplasma pagocytophilumandAnaplasma bovis.
A microcosm experiment was conducted to study the effects of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) on the growth and the nitrogen and phosphorus absorption of sweet corn seedlings to provide reference for the development of AMF. Sweet corn seedlings (Zea maysvar.rugoseBonaf) were inoculated with 6 AMF species,Funneliformis mosseae(Fm),Gigaspora margarita(Gm),Acaulospora scrobiculata(As),Corymbiglomus tortuosum(Ct),Diversispora epigaea(De) andRhizophagus intraradices(Ri), and their growth and uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus were observed. The results showed that the plant height, root length, aboveground fresh quality, aboveground biomass and phosphorus accumulation of sweet corn seedlings inoculated with De were the highest and significantly higher than those of other treatments, and that the stem diameter and aboveground nitrogen accumulation of sweet corn seedlings inoculated with De also reached a higher level. The principal component analysis showed that the comprehensive performance of sweet corn seedlings inoculated with De was the best. Therefore, when sweet corn is planted in the field, it is recommended to inoculate sweet corn with De, which is more conducive to the growth of sweet corn and the accumulation of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in sweet corn.
In order to understand self-pollination and cross-pollination of two camellia species,Camellia vietnamensisandCamellia furfuraceain Hainan,C. furfuraceaandC. vietnamensiswere self pollinated, orC. furfuraceawas pollinated with the pollen ofC. vietnamensisfor crossing, and the pistils were sampled after different days of pollination to determine their dynamic changes in endogenous hormones, gibberellin (GA3), indole acetic acid (IAA), abscisic acid (ABA) and zeatin nucleoside (ZR), by using an enzyme-linked immunoassay. The results show that after the pollen tube enters the embryo sac, the level of IAA is reduced, which inhibits the growth of the pollen tube in the late stage, while the lower level of GA3inhibits the growth of the pollen tube. When the pollen tube enters the embryo sac, high levels of GA3may inhibit the growth of pollen tubes and the release of gametophytes, but high levels of ZR greatly promote the normal growth of pollen tubes in the stigma, and high levels of ABA greatly promote the growth and fertilization of pollen tubes. The imbalance of endogenous hormones plays a decisive role in the incompatibility of self-pollination of bothC. furfuraceaandC. vietnamensisin Hainan.
Wanquan River Basin constitutes the most important ecological barrier of Hainan province, and its ecological environment in the national economy of Hainan province and social development plays a pivotal role. However, the aquatic biological research in the basin has been less made in recent years, which greatly affected the ecological environment protection and species conservation in the basin. Therefore, a survey was made of the aquatic species and their related ecology in Yazhai section of Wanquan River Basin by using the methods of field monitoring, market survey and interview. The survey showed that the water at the Yazhai section of Wanquan River is high in quality, meeting the Class 3 of the national surface water standards, and is abundant in aquatic species with high biomass. Among the six sampling sites set up in the Yazhai section of Wanquan River Basin a total of 137 phyla of phytoplankton were collected, of which green algae species are the most abundant (60 species), accounting for 40.80% of the total phytoplankton species, and 6 types and 30 species of zooplankton were collected, of which rotifer species were most abundant (13 species), accounting for 43.33% of the total zooplankton species. There were 4 types and 14 species of zoobenthos collected, of which arthropod species were most abundant (6 species), accounting for 42.86% of the total zoobenthos species. There were 12 orders, 41 families, 68 genera and 82 species of fish collected, of which the orders of perch and cyprinid were most abundant, accounting for 45% and 27% of the total fish orders, respectively. There were 18 families and 48 species of aquatic vascular plants, of which gramineous plant species were most abundant (12 species), accounting for 25% of the total species of aquatic vascular plants. Comprehensive analysis of the diversity indexes of zooplankton, phytoplankton, zoobenthos and fish showed that the aquatic biodiversity in Yazhai section of Wanquan River is rich.
In order to have a basic picture of the birds at Hainan Xinying Mangrove National Wetland Park in Danzhou, Hainan, a combination of point counts and line transects was used to estimate the bird diversity at Hainan Xinying Mangrove National Wetland Park from January to December 2016, and a total of 57 species of birds in 7 orders and 19 families were recorded. Among them three species were recorded as Near Threatened (NT) on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, namely black-tailed sandpiper (Limosa limosa), red-necked sandpiper (Calidris ruficollis) and the bent-billed sandpiper (Calidris ferruginea); one species was recorded as Vulnerable (VU), blue jade (Halcyon pileata); one species of Critically Endangered (CR) and one species of Endangered (EN) birds, namely spoonbill sandpiper (Calidris pygmaea) and black-faced spoonbill (Platalea minor), respectively, which are also listed as wild animals in Class I under state protection. There are six species of wildlife at Class II under state protection, namely white-breasted emerald (Halcyon smyrnensis), Eurasian curlew (Numeniu sarquata), Osprey (Pandion haliaetus), semipalmated sandpiper (Limnodromus semipalmatus), Eurasian spoonbill (Platalea leucorodia), and white-bellied harrier (Circus spilonotus). The number of birds tended to be in the order of winter > autumn > spring > summer, and the number of bird species was in the order of spring > autumn > winter > summer. Birds were highest in number in January-March, November and December with over 300 birds, and lowest in May-July with less than 100 birds. The number of bird species (35), diversity index (2.7) and evenness index (0.76) were higher in spring than in the other three seasons, while the highest dominance index was in summer (0.17) and autumn (0.17). The survey found three species of birds for the first time at the park: the bent-billed shorebird (C. ferruginea), the grey-faced buzzard (Butastur indicus) and the black-cushioned oriole (Oriolus chinensis), which are new records of birds at the Hainan Xinying Mangrove National Wetland Park, but in general, the proportion of birds under state protection at the park is lower than the national average, and the species and number of raptors are also lower than the average of raptors distributed in China, indicating that the protected area is not rich enough in species diversity and that the top taxa of the food chain are still lacking. This survey provides some data for the next long-term monitoring and evaluation of birds at the park, and the reasons for changes in the global migration of birds throughout the year were analyzed, based on which targeted conservation recommendations are proposed.
Giant clams are the largest living marine bivalves inhabiting coral reefs, and perform a significant ecological role in maintaining the balance of coral reef ecosystem. In recent years, giant clams in the waters at Xisha Islands, China are seriously threatened due to overfishing and the deterioration of the marine environment in the coastal areas. In order to master the present status of giant clam resources at Xisha Islands, a survey of giant clams in the waters at the main islands of Xisha Islands were made by using the method of line intercept transect to determine the species and distribution of the giant clams at Xisha Islands in the South China Sea from June to July 2017, and then analyze the correlation of the giant clams with the environment in the waters at the main islands of Xisha Islands. The results showed that there were four species of the giant clams in the survey area, includingTridacna squamosa,Tridacna crocea,Tridacna maximaandHippopus hippopus, accounting for 71.9%, 15.6%, 9.4% and 3.1% of the total giant clams, respectively. The giant clams in the waters of different main islands of Xisha Islands are significantly different in habitat density and species diversity index. The average density of the giant clams is 0.026 ind/m2. Correlation analysis showed that there was a significant positive correlation between habitat density and coral reef coverage (P<0.05,R2= 0.7065). This shows that coral reef coverage is an important factor affecting the distribution of giant clams. This result can provide scientific basis for the conservation of giant clam resources in Xisha Islands in China.
Mudskipper is a fish of goby family with high economic and ecological value. Markers of mitochondrial control region were used to analyze genetic diversity, genetic structure, and demographic history among nine populations of three mudskipper species, such asPeriophthalmus modestus,Boleophthalmus pectinirostrisandPeriophthalmus magnuspinnatus, for better conservation of Mudskipper resources. All samples were separately collected from nine localities (Haikou, Wenchang, Chengmai, Lingao, Danzhou, Changjiang, Dongfang, Ledong and Sanya) in Hainan Island. As a result, we have obtained 195D-Loopgene sequences of with a length of 836 bp from all the Mudskipper samples. The analysis showed thatP. modestusis highest in genetic diversity withB. pectinirostrisbeing the lowest among the three mudskipper species. The genetic differentiation indexes (Fst) ofP. modestusindicated that there are moderate genetic differentiations between Sanya and each of Lingao, Dongfang and Ledong populations. The analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) ofP. modestussuggested the absence of genetic variation within populations. TheFstofB. pectinirostrisshowed that there is a high genetic differentiation between Wenchang and Dongfang populations, and the AMOVA ofB. pectinirostrissuggested the existence of moderate difference within populations. The genetic distance analysis of the three mudskipper species showed thatP. modestusandP. magnuspinnatuspopulations had the closest relationship and could be distinguished byD-Loopgene sequences. The neutrality test and mismatch distribution analysis showed that the Wenchang population ofB. pectinirostriswas obviously expanded in its evolution. All the results showed that genetic resources ofB. pectinirostrisamong three mudskippers populations should be conserved as a priority.
In order to explore the preservation conditions ofLysinibacillus boronitoleransYS11 and its effect on the diversity and abundance of intestinal microorganisms in tilapia for the research and development of microbial feed additives. Four protectants, i.e. trehalose, lactose, sucrose and skim milk powder, were selected and optimized by concentration gradient. The results confirmed that YS11 maintained a high survival rate after drying in 10% trehalose. Tilapia fingerlings were fed with feeds containing bacterial fermentation broth, and after 70 days of feeding, high-throughput sequencing was performed to observe the effect of the feeds on tilapia intestinal microbial community. The results showed that the feed containing YS11 changed the tilapia gut microbiota and its diversity, increased the abundance of beneficial bacteria in the tilapia gut, and decreased the abundance of some potential pathogenic bacteria. These results confirmed that 10% trehalose was the best freeze-drying protectant.L. boronitoleranscan regulate the intestinal microbiota, promote the growth of probiotics, and inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
Tunas are species of bony fish belonging to the family Scombridae, order Perciformes, and class Osteichthyes. They are high trophic predators with marine migratory behavior. Tunas have acquired various distinct biological traits in response to the pressures of human overfishing and the variable marine environments. Focused on Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus), bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus), and yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacores), the most popular research methodologies and important research results in tuna biology, including age and growth, feeding, and reproduction are reviewed. The unique biological properties of tunas to boost the population's fitness (e.g., multiple growth inflection points, opportunistic predators, and multiple reproductive strategies, etc.) are illustrated. At the same time, the existing shortcomings in the field of tuna biology research are analyzed, based on which suggestions for future research, regarding research methods, equipment and technologies are hence proposed.
In order to determine the pathogen of leaf blight of kidney plant (Clerodendranthus spicatus(Thunb.) C.Y.Wu), the kidney plant leaves infected with leaf blight were sampled from a kidney plant producing area in Yunnan, and one strain of the pathogen was isolated from the samples and then identified morphologically and molecularly. The results showed that the pathogen cultured on the PDA medium was white in colony, and well developed in aerial mycelia. The colony in the lower part was pale pink initially and then turned yellow-brown. The apical cells of the conidia were uncinate, and the mature macroconidia have 3~5 septa. The pathogen isolated was inoculated onto the healthy plant leaves ofC. spicatus. After several days of moist culture, dark-brown lesions appeared at the inoculated sites of the leaves, which were consistent with the field symptoms. Genomic DNA of the pathogen was amplified by using fungal rDNA-ITS universal primers ITS1/ITS4 and analyzed by homology analysis. The results showed that the pathogen isolated was clustered into the same branch withFusarium nematophilum,F. equiseti,F. chlamydosporumandF. longip, and had a nucleic acid sequence homology of 99.40%−99.60%. The morphological observation, ITS sequence analysis and establishment of Koch’s postulates showed that the pathogen was preliminarily identified asF. oxysporum.
Environmental stimulus and DNA replication may cause DNA mismatch and thus genomic instability, which must be repaired by organisms. All organisms evolve DNA repair systems to cope with these damages. MutL/MutS is the key DNA repair system of bacteria, but its function remains unknown inXanthomonas oryzaepv.oryzae(Xoo). Whether MutL/MutS is involved in DNA repair and virulence inXooneeds further studies.MutLmutant and its complementary strain were constructed, and their virulence and mutation rates were analyzed. Results showed thatMutLmutation increasedXoomutation rates under H2O2stress, indicating thatMutLis important for DNA repair during the stress. It was also found thatMutLmutation reducedXooinfection ability in rice leaves, suggesting thatMutLis required forXoo-rice interaction. In summary,MutLis involved in DNA repair inXoo, and is also vital forXoovirulence.
Supervisor:Department of education of Hainan Province
Sponsor:Hainan University
ISSN1674-7054
CN46-1078/S
- 1
One-step Oxidative Folding and nAChR Blocking Activity of Conotoxin Lv68
LI Cheng,ZHANG Yu,LUO An,JU Shuang,FU Ying,LUO Sulan - 2ZHANG Zhuandan,XIAO Zhengpan,WU Xinli,SUN Yan,LUO Ying,WU Hao,WEI Shuangshuang,PEI Yechun,WANG Dayong
- 3
Spatial Distribution of Arecoline Synthesis Precursors and Analysis of Arecoline Synthesis Pathway
XU Hang,LIU Xianqing,YUAN Honglun,LUO Jie - 4
Immunogenicity ofAeromonas veroniiΔexsA1 Attenuated Strains
SHENG Qianglong,XU Yike,LIU Chaolun,LI Hong,MA Xiang,TANG Yanqiong,LIU Zhu - 5XIA Xi






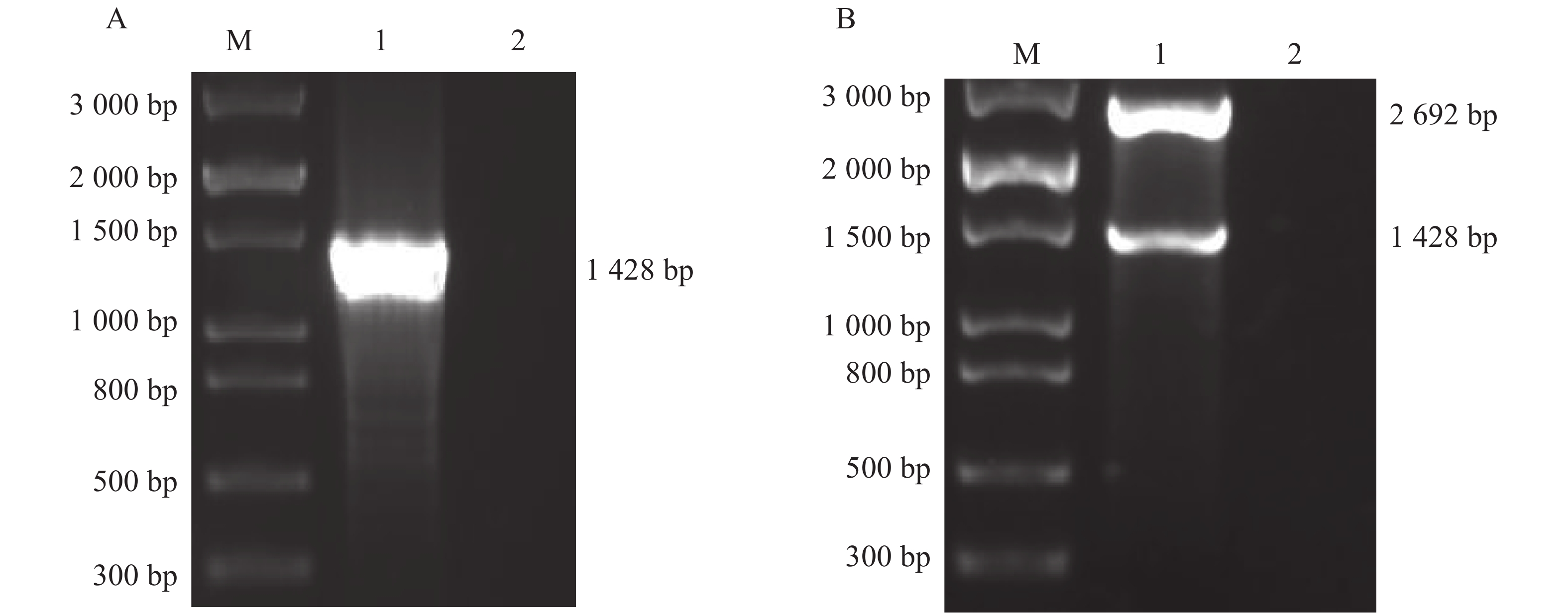

 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML











































 PDF 217KB
PDF 217KB















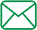 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS